Continuous Panel Manufacturing Methods
There are several methods for continuous panel manufacturing, including:
Continuous Press method: This involves the use of a continuous press machine to produce panels from a continuous sheet of material, such as wood, metal, or composite materials. The material is fed into the sandwich panel machine, and a series of rollers press it into the desired shape and size.
Continuous Laminating method: This involves the use of a continuous laminating machine to produce panels by bonding together layers of material, such as wood veneers, paper, or composite materials. The layers are fed into the machine and are pressed together using heat and pressure to create the panel.
Continuous Cast method: This involves the use of a continuous casting machine to produce panels from a continuous stream of molten material, such as metal or plastic. The material is poured into a mold and is cooled and solidified as it moves through the machine, producing a panel of the desired shape and size.
Continuous Extrusion method: This involves the use of a continuous extrusion machine to produce panels from a continuous stream of material, such as plastic or composite materials. The material is fed into the sandwich panel cutting machine and is forced through a die to produce a panel of the desired shape and size.
Continuous Insulation method: This involves the use of a continuous insulation machine to produce panels by injecting insulation material, such as foam or fiberglass, into a panel-shaped mold. The insulation material is then cured and the panel is removed from the mold.
Discontinuous Panel Manufacturing Methods
There are several methods for discontinuous panel manufacturing, including:
Layered construction method: This involves building up layers of material, such as wood or composite materials, and bonding them together to form a panel. The layers can be cut to size and then glued or pressed together to form the panel.
Sandwich panel method: This involves bonding together two or more layers of material, such as wood or metal, with a core layer of insulation material, such as foam or honeycomb. The layers are bonded together using adhesives or mechanical fasteners to form a panel.
Thermoforming method: This involves heating a sheet of plastic or composite material until it is pliable, and then forming it into the desired shape and size using a mold or a set of dies. The material is then cooled and the panel is removed from the mold.
Injection molding method: This involves injecting a melted material, such as plastic or composite materials, into a mold. The material is allowed to cool and solidify, and the panel is removed from the mold.
Blow molding method: This involves heating a tube of plastic or composite material until it is pliable, and then using air pressure to blow it into the desired shape and size using a mold. The material is then cooled and the panel is removed from the mold.
Continuous Puf Panel Production line Manufacturing Process
Continuous PUF (polyurethane foam) panel production involves the use of a sandwich panel production line to manufacture panels made of polyurethane foam. The sandwich panel manufacturing process typically involves the following steps:
Preparation of raw materials: The raw materials, including isocyanate, polyol, and blowing agents, are weighed and mixed according to the desired formulation.
Mixing and foaming: The mixed raw materials are fed into a mixing head, where they are mixed and heated to initiate the foaming reaction. The mixture expands as it foams, filling a mold or a panel-shaped cavity.
Curing and cooling: The foam is allowed to cure and cool in the mold or cavity, forming a solid panel.
Trimming and finishing: The panel is removed from the mold or cavity and trimmed to the desired size and shape. Any necessary finishing operations, such as sanding or coating, are performed.
Quality control: The finished panels are inspected for quality and any necessary adjustments are made.
Packaging and shipping: The finished panels are packaged and shipped to the customer.


 CN
CN
 EN
EN
 fr
fr  de
de  es
es  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  ar
ar  th
th  pl
pl  ro
ro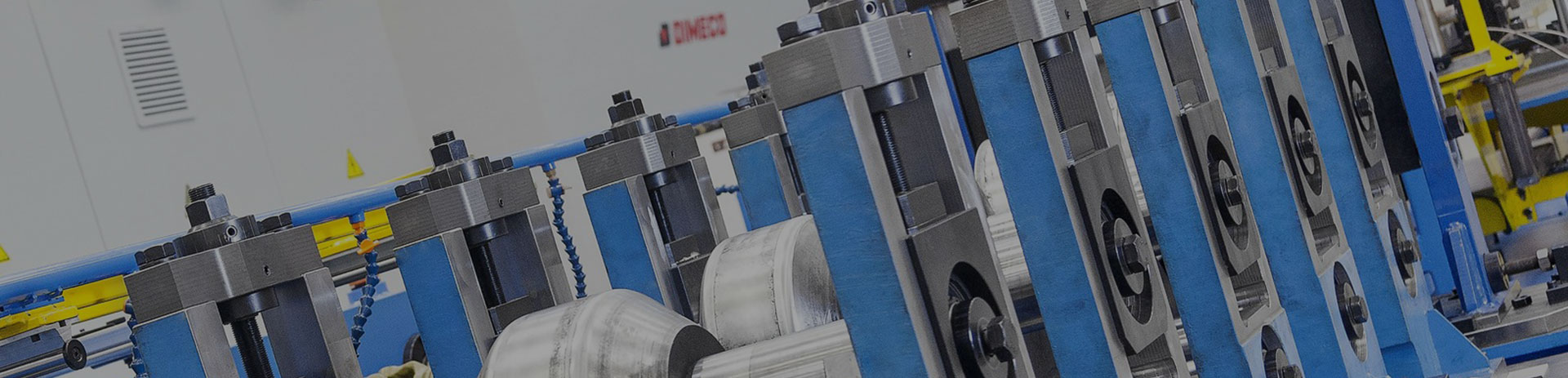 







 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  #1809, Jianhu Rd, Keqiao, Shaoxing, Zhejiang, China
#1809, Jianhu Rd, Keqiao, Shaoxing, Zhejiang, China 